Algorithmic verification
Algorithmic verification
Frédéric Herbreteau, Bordeaux INP/LaBRI (frederic.herbreteau@bordeaux-inp.fr)
Objective
- Use model-checking to assert the correctness of a system
- from a model $M$: a set of runs given as a transition system
- and a specification $\varphi$ \(M \models \varphi\)
- The specification $\varphi$ shall specify which runs are correct and which are not
- A dedicated algorithm is then use to decide wether $M \models \varphi$ or not
Verification of invariance properties
Algorithmic verification of invariance properties
- Invariance properties that involve only one state (not a sequence of states)
- Must hold in every state of the model
Example:
- mutual exclusion: no state with both $\textcolor{blue}{cs_1}$ and $\textcolor{red}{cs_2}$
Exercise: Give an algorithm to check an invariance property over a finite transition system
Verification of temporal properties
Temporal formulas
| $\varphi ::= p \, | \, \lnot \varphi \, | \, \varphi \land \varphi \, | \varphi \lor \varphi \, | \, \varphi \implies \varphi \, | \, \Box \varphi \, | \, \Diamond \varphi \qquad\qquad \text{with } p \in AP$ |
- $\Box$ means “always”
- $\Diamond$ means “eventually”
Example:
- $\Box \lnot (\textcolor{blue}{cs_1} \land \textcolor{red}{cs_2})$
- $\Diamond \textcolor{blue}{cs_1} \land \Diamond \textcolor{red}{cs_2}$
- $\Box (\textcolor{blue}{req_1} \implies \Diamond \textcolor{blue}{cs_1})$
TLA+ operators: ~, /\, \/, =>, [], <>
Semantics of temporal formulas
Expressed over infinite sequences of observations (sets of labels):
Example: labels ${\textcolor{blue}{cs_1}$, $\textcolor{red}{cs_2}}$ trace: {} {} {$\textcolor{blue}{cs_1}$} {} {$\textcolor{red}{cs_2}$} {} {} … {} {$\textcolor{red}{cs_2}$} {} {$\textcolor{blue}{cs_1}$} {} {} {$\textcolor{blue}{cs_1}$, $\textcolor{red}{cs_2}$} {} {} …
$\sigma$ an infinite trace, $\sigma[i]$ its value in $i$, $\sigma[i…]$ its suffix from $i$
- $\sigma \models p$ if $p \in \sigma[1]$
- $\sigma \models \lnot \varphi$ if $\sigma \not\models \varphi$
- $\sigma \models \varphi_1 \land \varphi_2$ if $\sigma \models \varphi_1$ and $\sigma \models \varphi_2$
- $\sigma \models \Box \varphi$ if $\sigma[i…] \models \varphi$ for every $i \ge 1$
- $\sigma \models \Diamond \varphi$ if there exists $i \ge 1$ such that $\sigma[i…] \models \varphi$
Semantics over a transition system
Definition A transition system $M$ satisfies a temporal formula $\varphi$ ($M \models \varphi$) if $\sigma \models \varphi$ for every infinite trace $\sigma$ from an initial state of $M$.
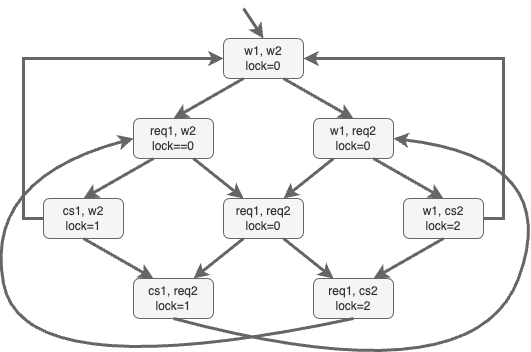
Example: Which formulas below are satisfied by the model to the right?
- $\Box \lnot (\textcolor{blue}{cs_1} \land \textcolor{red}{cs_2})$
- $\Diamond \textcolor{blue}{cs_1} \land \Diamond \textcolor{red}{cs_2}$
- $\Box (\textcolor{blue}{req_1} \implies \Diamond \textcolor{blue}{cs_1})$
Algorithmic verification of temporal formulas (overview)
Goal: given $M$ and $\varphi$, decide whether $M \models \varphi$
Algorithm:
- From $\varphi$ compute a Büchi automaton $\mathcal{A}_{\lnot \phi}$
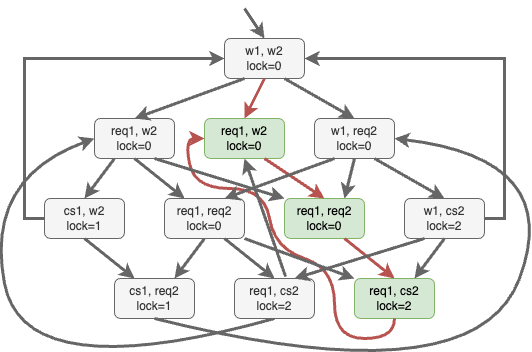
- Compute the product $\mathcal{B} = M \otimes \mathcal{A}_{\lnot \phi}$
- Decide whether $\mathcal{L}(\mathcal{B}) = \emptyset$
From TL formulas to Büchi automata
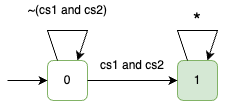
Example: $\Box \lnot (\textcolor{blue}{cs_1} \land \textcolor{red}{cs_2})$
- {} {$\textcolor{blue}{cs_1}$} {} {} {$\textcolor{red}{cs_2}$} {} {$\textcolor{blue}{cs_1}$} {} {} …
- {} {} {$\textcolor{red}{cs_2}$} {} {$\textcolor{blue}{cs_1}$, $\textcolor{red}{cs_2}$} {} {$\textcolor{blue}{cs_1}$} {} …
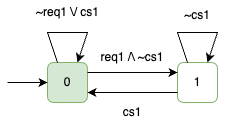
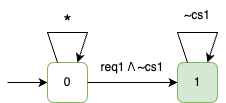
Example: $\Box (\textcolor{blue}{req_1} \rightsquigarrow \textcolor{blue}{cs_1})$
- {} {$\textcolor{blue}{req_1}$} {} {} {$\textcolor{blue}{cs_1}$} {} {$\textcolor{blue}{cs_1}$} {} {} {$\textcolor{blue}{req_1}$, $\textcolor{blue}{cs_1}$} {} …
- {} {} {$\textcolor{blue}{req_1}$} {$\textcolor{blue}{cs_1}$} {} {$\textcolor{blue}{req_1}$} {} {} {$\textcolor{blue}{req_1}$} {} {}…
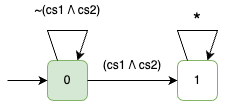
Product $M \otimes \mathcal{A}_{\lnot \varphi}$ (1/2)
Example: $\Box \lnot (\textcolor{blue}{cs_1} \land \textcolor{red}{cs_2})$
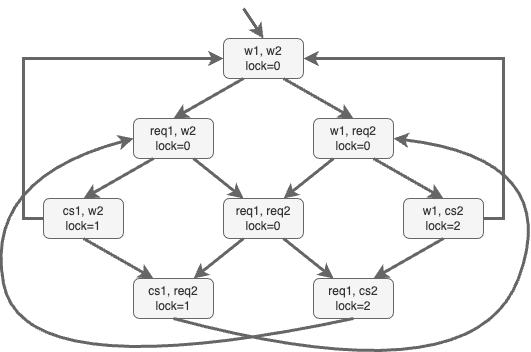
Product $M \otimes \mathcal{A}_{\lnot \varphi}$ (2/2)
Example: $\Box (\textcolor{blue}{req_1} \rightsquigarrow \textcolor{blue}{cs_1})$
Checking if $\mathcal{L}(M \otimes \mathcal{A}_{\lnot \varphi}) = \emptyset$
-
$\mathcal{L}(M \otimes \mathcal{A}_{\lnot \varphi}) \neq \emptyset$ iff there is an infinite run that visits an accepting state infinitely many times
-
What is the structure of a such a run?
Exercise: give an algorithm that decides if $\mathcal{L}(M \otimes \mathcal{A}_{\lnot \varphi}) \neq \emptyset$
- How to include fairness constraints in the model-checking process?
Complexity
*Theorem: the TL model-checking problem is PSPACE-complete
Overall complexity of the verification algorithm:
-
TL to Büchi automaton: $ \mathcal{A}_{\lnot \varphi} = 2^{\mathcal{O}( \varphi )}$ -
Product: $ M \otimes \mathcal{A}_{\lnot \varphi} = \mathcal{O}( M \times \mathcal{A}_{\lnot \varphi} )$ -
Emptiness checking: $\mathcal{O}( M \otimes \mathcal{A}_{\lnot \varphi} )$ -
Overall complexity: $\mathcal{O}( M \times 2^{ \varphi })$